When it comes to managing your financial records and filing taxes, understanding the difference between an IRS transcript and a W-2 form is essential.
While both provide crucial information about your income and tax filings, they serve distinct purposes and are issued by different entities.
Let’s break down the Difference Between IRS Transcript and W-2 Form.
Difference Between IRS Transcript and W-2 Form
Below are the differences between both these things to make everything clear.
What Is a W-2 Form?
A W-2 form, also known as the Wage and Tax Statement, is an official document provided by employers to employees.
It outlines the total wages earned during the year, along with the taxes withheld for federal, state, and local governments.
Key Components of a W-2 Form:
- Employee Information: Name, Social Security number, and address.
- Employer Details: Employer’s name, address, and Employer Identification Number (EIN).
- Income Details: Total wages, tips, and other compensation.
- Tax Withholding: Federal, state, Social Security, and Medicare taxes withheld.
The W-2 is crucial for employees when filing their annual tax returns, as it directly reports income earned and taxes paid to the IRS.
Employers are required to send W-2 forms by January 31 each year.
What Is An IRS Transcript?
An IRS transcript is a summary document generated by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) that provides details about your tax filings and financial history.
Types of IRS Transcripts:
- Tax Return Transcript: Summarizes data from your filed tax return.
- Wage and Income Transcript: Displays income information from sources like W-2s, 1099s, and other tax forms.
- Account Transcript: Shows tax account activity, including adjustments and balances.
- Record of Account Transcript: Combines the Tax Return and Account Transcripts.
IRS transcripts are commonly used for loan applications, income verification, or resolving tax issues.

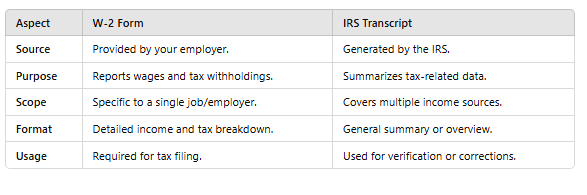
The Key Differences Between an IRS Transcript and a W-2 Form
When to Use a W-2 Form?
You’ll need a W-2 form for:
- Filing your tax return.
- Applying for loans or mortgages to verify income.
- Understanding your yearly income and tax withholdings.
If you misplace your W-2, consider contacting your employer or accessing an online payroll system.
Alternatively, tools like a W2 form generator can assist in preparing supplemental documents for organizational purposes.
When to Use an IRS Transcript?
An IRS transcript is ideal for:
- Verifying income when your W-2 is unavailable.
- Reviewing past tax returns for accuracy.
- Providing income proof for financial institutions.
- Resolving discrepancies with the IRS.
For instance, if you lost your W-2 and need to file your taxes, you can request a Wage and Income Transcript from the IRS, which summarizes your W-2 details and other income data.
Can You Use Both?
Yes! While a W-2 form is required for filing your taxes, an IRS transcript can complement it in certain situations:
- Verification: Use a transcript to confirm the accuracy of your W-2 form.
- Record Keeping: Maintain transcripts for financial planning or audit protection.
- Replacement: If your W-2 is lost, the IRS transcript can act as a temporary substitute.
Simplify Financial Tasks with Modern Tools
Managing financial records can be overwhelming, but innovative tools can help.
For instance, a bank statement generator can organize your income and expenses, while payroll management systems often integrate W-2 generation for easy access.
Final Verdict:
Understanding the difference between IRS transcript and W-2 form is key to managing your taxes effectively.
While the W-2 form is an essential document for filing your taxes, the IRS transcript serves as a broader financial overview.
Together, these tools can simplify your tax filing process and ensure accuracy in your financial records.